Understanding Stomach Cancer Treatments: A Comprehensive Guide
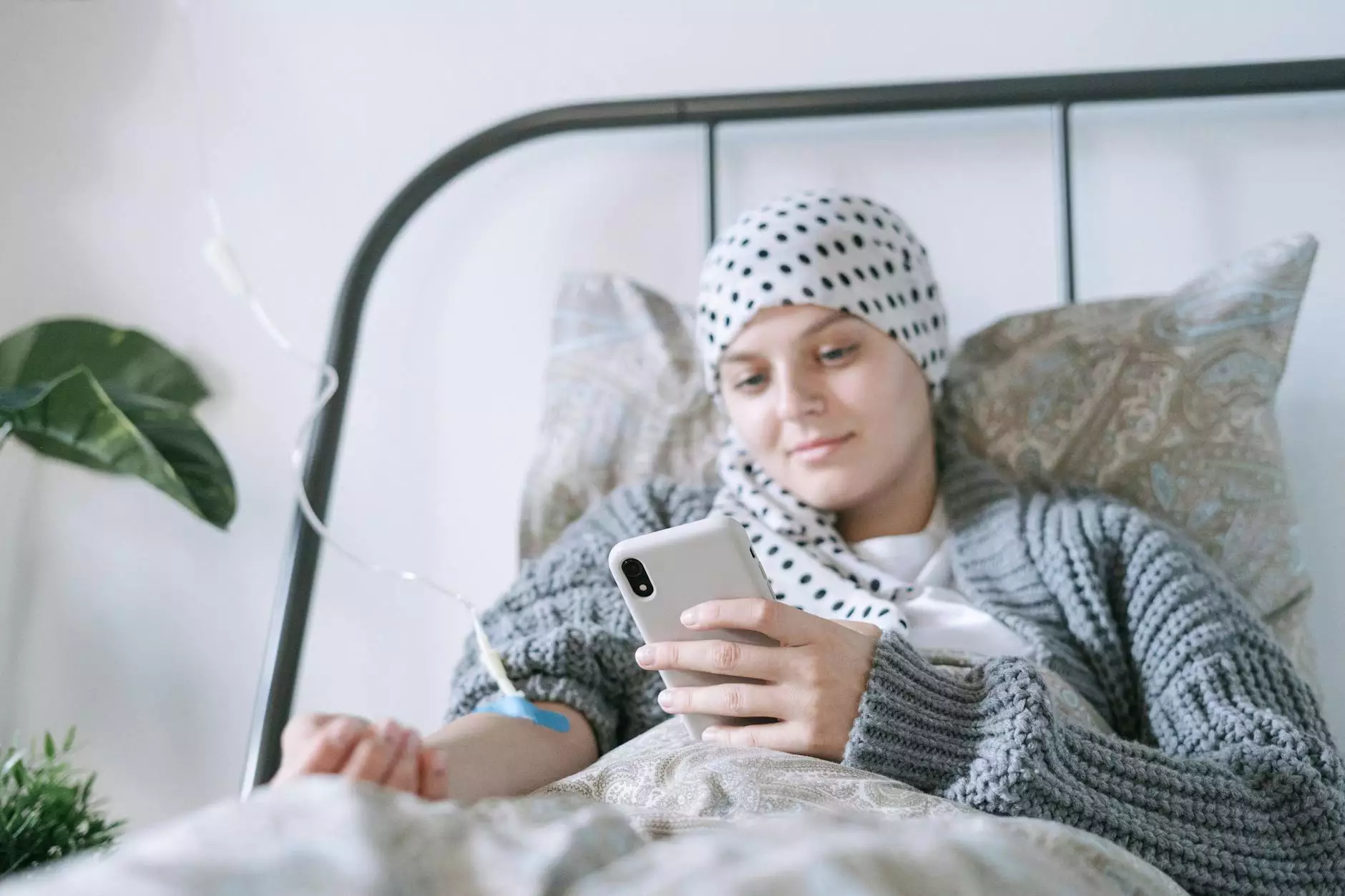

Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, remains one of the more challenging cancers to treat, primarily due to its often-late diagnosis and complex pathology. As a patient or a caregiver, understanding the available stomach cancer treatments is crucial for making informed decisions. This article offers an in-depth look at the various treatment options, helping you navigate the healthcare landscape effectively.
What is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer originates in the stomach lining but can penetrate deeper into the wall of the stomach and spread to nearby organs. Early detection is often complex, as symptoms may be vague or mistaken for other conditions. Some common risk factors include:
- Family history of gastric cancer
- Infection with Helicobacter pylori
- Chronic atrophic gastritis
- Pernicious anemia
- Smoking
- High salt diets
Diagnosis of Stomach Cancer
The diagnosis of stomach cancer typically involves a combination of procedures:
- Endoscopy: A thin, flexible tube with a camera allows doctors to visualize the stomach lining and take biopsy samples.
- Imaging Tests: CT scans, MRIs, and PET scans help determine the cancer's extent.
- Biopsies: Tissue samples are analyzed to confirm cancer presence and type.
Types of Stomach Cancer Treatments
Stomach cancer management is multi-faceted, employing a combination of the following treatment modalities:
Surgery
Surgical intervention is often the frontline treatment for stomach cancer, especially in early-stage cases. Key surgical options include:
- Partial Gastrectomy: Removal of a section of the stomach.
- Total Gastrectomy: Complete removal of the stomach, typically followed by reconstruction of the digestive tract.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive techniques with smaller incisions, reducing recovery time.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy utilizes high-energy radiation to kill cancer cells. It's often used in conjunction with surgery to reduce the risk of recurrence. Various types include:
- External Beam Radiation: Targets the tumor from outside the body.
- Brachytherapy: Involves placing radioactive material directly inside the stomach.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy employs powerful drugs to eliminate cancer cells. This systemic treatment may be used preoperatively (neoadjuvant) or postoperatively (adjuvant) to enhance the effectiveness of surgery. Commonly used chemotherapy drugs for stomach cancer include:
- Fluorouracil
- Cisplatin
- Docetaxel
- Capecitabine
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapies focus on specific molecular targets associated with cancer. These may provide additional treatment avenues for patients with advanced gastric cancer. Examples include drugs that target HER2 protein in HER2-positive stomach cancers:
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin): Aims at HER2-positive tumors.
- Ramucirumab: Targets blood vessel growth to the tumor.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy harnesses the body’s immune system to fight cancer. Certain checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in treating metastatic stomach cancer. These include:
- Pembrolizumab (Keytruda)
- Nivolumab (Opdivo)
Latest Advances in Stomach Cancer Treatments
Ongoing research continues to pave the way for innovative approaches in stomach cancer treatments. Some exciting developments to consider include:
Personalized Medicine
With advancements in genetic testing, treatments are increasingly tailored to the specific genetic makeup of the patient's tumor. Genomic profiling allows oncologists to identify actionable mutations, leading to targeted treatment strategies.
Combination Therapies
Researchers are exploring the effectiveness of combining different treatments, such as chemotherapy and immunotherapy, to enhance patient outcomes. Clinical trials are a vital avenue for accessing groundbreaking treatment combinations.
Clinical Trials: The Future of Stomach Cancer Treatments
Participating in clinical trials can provide patients access to cutting-edge treatments and therapies. ClinicalTrials.gov offers a database of ongoing trials that include innovative drugs and treatment methodologies. Patients are encouraged to discuss clinical trial options with their oncologists.
Psychosocial Support for Patients and Families
Coping with a stomach cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming. Support services, including counseling, support groups, and educational resources, play a crucial role in the treatment journey. Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional relief and practical advice.
Living with Stomach Cancer
Adapting to life after a stomach cancer diagnosis involves both physical and emotional adjustments. Here are key aspects to consider:
Nutritional Support
Due to potential changes in digestion after treatment, working with a nutritionist to establish a balanced diet is essential. Proper nutrition can enhance recovery and overall quality of life.
Regular Follow-up Care
Once treatment concludes, regular follow-up appointments are vital for monitoring health and detecting any signs of recurrence. Patients should maintain a schedule of visits with their healthcare team.
Conclusion: Empowering Your Journey
Navigating stomach cancer treatments can be a complex journey fraught with challenges. However, with the right information, support, and advanced medical options, patients can approach their treatment with empowerment and hope. Always consult with a medical professional to understand the best options tailored to your specific situation.
Resources for Further Information
For more information on stomach cancer treatments, patients can explore:
- National Cancer Institute
- American Cancer Society
- American Association for Cancer Research
By staying informed and connected, patients and families can manage the complexities of stomach cancer with knowledge and strength.